Sleeping Well in the Age of Stress:Part 1
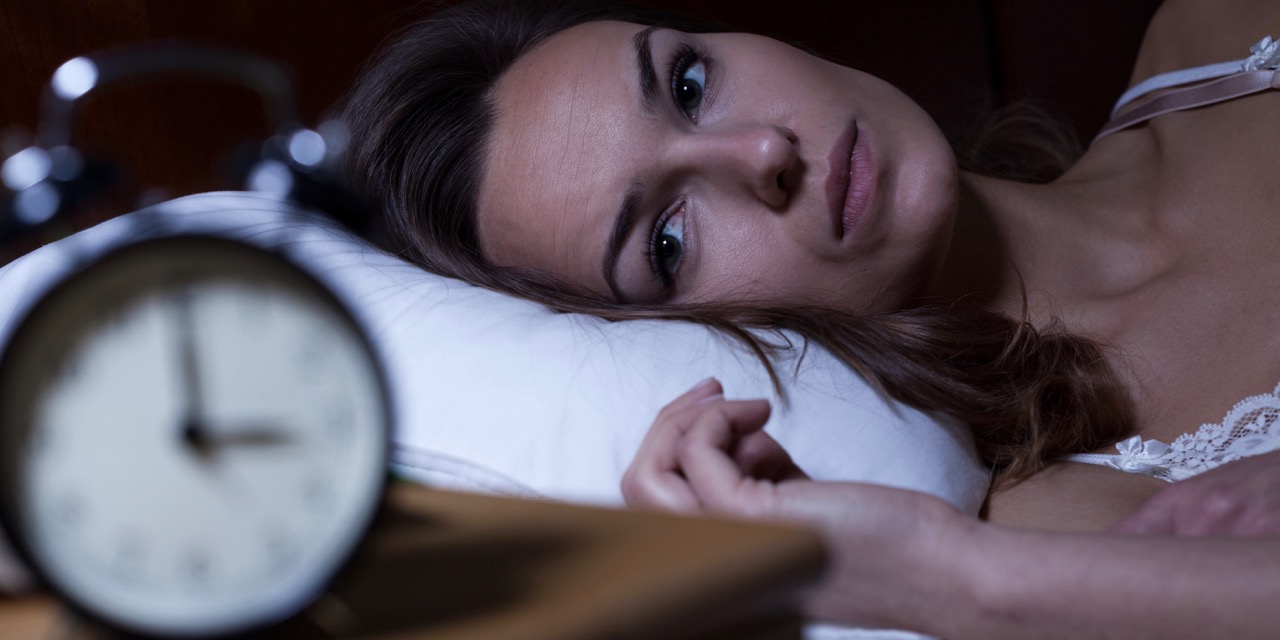
It’s 3:00 a.m. and you’re wide awake.
In six hours you’re going to give the biggest presentation of your career. That is, after you get your kids out of bed, dressed, and off to school. Oh, right. You have to drop your husband at the airport. What else? You start your to-do list. Did you pay your water bill? What about the kids’ camp fees? Did you buy cereal yesterday?
Stop! If only you could nod off. You close your eyes, hoping that action in itself stops the wheels in your brain from turning. Suddenly, you hear a drip of water. Your tired mind turns toward the leaky bathroom faucet.
Drip.
Drip.
Pause. Wait for it.
Drip.
We’ve all been there right? It’s terrible. On the other hand, we know what a big night of sleep can do for you. Our energy levels reset, allowing us to invite new possibilities into our lives. There’s nothing like it, especially when you can get the big sleep every night.
Unfortunately, many of us are not getting enough sleep. The American Sleep Association estimates that as many as 70 million adults in the United States could suffer from some kind of sleep disorder that either shortens the duration of their sleep or makes them wake up un-rested.
Sleep deprivation can have several different causes, including health conditions, lifestyle choices, and stress. Stress is a big one. There are now different treatment options based on scientific research available for various sleep disorders. Sleep hygiene, for instance, suggests establishing a bedtime routine and schedule, and adopting other good sleep habits could improve the incidence of sleep disorders like insomnia. Bear in mind, however, that sleep hygiene alone may not be enough to treat such conditions.
We Learned From The Best
We wanted to find out more about the world of sleep and how it regenerates our bodies, as well as the common causes of sleep deprivation and available treatment options. So we spoke to a leading expert in the field of sleep medicine.
Dr. Rohit Budhiraja is an assistant professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, the director of Brigham and Women’s Hospital’s sleep clinic, and a faculty member in Division of Sleep and Circadian Disorders and Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine in Boston, MA.
Budhiraja’s main field of study is sleep apnea and other sleep-related breathing disorders. However, he was able to go over everything from how sleep helps regenerate the body and mind. He also explained how temperature, light, and calming (what he calls TLC) is so important to get a good night’s sleep. “On average, most people need seven or eight hours of sleep,” says Budhiraja.
Let us share what we learned with you, starting with the basics.

What is Sleep?
Animals as small as the honeybee and as large as the blue whale fall asleep every day and perform noticeably better when well-rested. But what exactly causes us to feel sleepy and doze off? And how did most of the animal kingdom evolve the need for sleep in the first place?
Here’s the succinct definition of sleep taken from the Merriam-Webster Medical Dictionary, “…the natural periodic suspension of consciousness during which the powers of the body are restored.”
There is evidence that sleep was handed down to most animals from a common ancestor nearly 700 million years ago. According to a New York Times profile on a 2014 study, “our nightly slumbers evolved from the rise and fall of our tiny oceangoing ancestors, as they swam up to the surface of the sea at twilight and then sank in a sleepy fall through the night.”
There are many reasons why this adaptation evolved. For one, it’s possible that sleep is meant to keep animals inactive at times when they were unlikely to find food and when their predators were most active. Sleep also affords the benefit of repairing and restoring the body, which allows animals to avoid predators more effectively and find food in their waking hours. Take a look at honeybees, which perform a “waggle dance” to tell other bees where food can be found. When bees are sleep-deprived, their dance is not as precise, making it more difficult for other bees to follow their directions.
35.2% of adults 18 and older report sleeping less than 7 hours every night.
– Center for Disease Control (CDC)
“Some historians and researchers believe that, centuries ago, humans followed biphasic or polyphasic schedules,” says Budhiraja. Biphasic sleep is when someone sleeps two separate times during a 24-hour period whereas polyphasic sleep is when someone sleeps multiple times (more than twice) in a 24-hour period. “Industrial Revolution and artificial lighting may have forced people to adopt monophasic schedules.” He went on to clarify that there is little evidence to suggest a polyphasic schedule is a good idea. As for biphasic sleep, there are several countries and cultures which still practice an afternoon nap or ‘siesta’.

How Sleep Works
While the exact mechanism for how sleep happens in humans is still unclear, the broad strokes are these: the hypothalamus generates the circadian rhythm—the inner clock that says we should sleep at night and be awake during the day—and triggers the release of melatonin, a compound that signals to our brain when we should be asleep.
Meanwhile, as our brain works hard during the day, another compound called adenosine is released by astrocytes. Adenosine accumulates in the brain and eventually reaches levels that trigger drowsiness. Melatonin and adenosine work together—and sometimes independently—to make us feel tired and crave sleep. When we’re asleep, adenosine levels decrease while melatonin stays high. When the circadian rhythm says it’s time to wake up, melatonin decreases and we become alert.
Why We Sleep
Memories
We know much more about why humans need sleep than other animals. One of the benefits humans get from sleep is the consolidation of memories. When we’re awake, we’re receiving sensory input from the things we see, hear, feel, and our brain forms connections between what is happening to us in real time and what we remember. According to Budhiraja, when we fall asleep our brains work on reclassifying the information we received during the day and cataloging our memories.
Much like a librarian takes the books in the return cart and places them in the correct shelf, the brain sorts through the events of the day and classifies the information into new areas. Not only does the brain place the information in the correct areas during sleep, it also removes unnecessary information by getting rid of those superfluous neural connections.
The woods are lovely, dark and deep, And I have promises to keep, But neither the woods nor those promises Are as important as some restorative sleep. – Dr. Budhiraja’s variation on Robert Frost’s poem
Restoration
Another reason we need sleep is to restore our bodies. “During sleep,” says Budhiraja, “our bodies relax and muscle tone decreases.” And when our muscles relax, the damaged tissue regenerates more efficiently. That’s why a good night’s sleep feels so good after an exhausting workout session.
Budhiraja goes on to explain that research points towards REM (rapid-eye-movement) sleep as the stage where much of the muscle recovery and memory consolidation happens. REM sleep—also called Stage R—is characterized by being the stage at which we dream. Typically, REM sleep happens 90 minutes after we first fall asleep.
First, we cycle through non-REM (NREM) stages of sleep—N1, N2, and N3—which bring us deeper and deeper into rest as our brain activity slows down. Once the REM stage is over, the cycle from stage N1 to stage R restarts, in a repetitive process that lasts approximately 90 minutes and happens multiple times per night.
“Your genes decide if you’re a 6-hour sleeper or a 9-hour sleeper,” says Budhiraja. Though doctors do recommend getting between 7 and 8 hours of sleep every night, there is no one-size-fits-all answer.
The body loses its rhythm without a fixed sleep and wake-up schedule.
-Dr. Rohit Budhiraja

Common Sleep Disorders
Though there are dozens of sleep disorders, as listed by the third edition of the International Classification of Sleep Disorders (ICSD-3), below we will discuss the three most common sleep disorders: insomnia, sleep apnea, and restless leg syndrome.
Insomnia
An individual is said to suffer from insomnia if they have trouble falling asleep or staying asleep throughout the night, if they wake up too early in the morning, or if the sleep they have is non-restorative. Almost 60 million Americans suffer from insomnia every year.
While primary insomnia—that is, insomnia that doesn’t appear to be caused by another disorder—is a problem for many people, in most cases, it is caused by or appears alongside a wide range of conditions, such as depression, heart disease, diabetes, and chronic pain.
| Treatments for Insomnia |
| Bad habits or poor lifestyle choices are some of the main causes of insomnia. Stress, no bedtime routine, irregular work schedules, and side effects from prescription medications can be the primary causes of this sleep disorder.
Sleep Hygiene is a collection of lifestyle changes that can improve sleep. These include: establishing a bedtime routine, eliminating the consumption of caffeine, alcohol, nicotine, and certain foods close to your bedtime, getting regular exercise and losing weight, limiting daytime nap times to 30 minutes, creating a welcoming sleep environment, and getting a lot of natural light during the day. If you continue to suffer from insomnia, other treatments include cognitive therapy such as light therapy or relaxation techniques. Finally, prescription or over-the-counter sleep medications can help you get to sleep but may also bring on other side effects. |
One in three over 30 year-olds have sleep apnea.
Sleep Apnea
Budhiraja then discussed sleep apnea. About one in three people over the age of 30 may have some degree of sleep apnea, with 13% of men and 6% of women having moderate to severe sleep-disordered breathing. “During an apnea episode, the muscles at the back of the throat and the tongue block the airway, causing the sleeper to stop breathing for seconds at a time,” says Budhiraja.
The Division of Sleep Medicine at Harvard Medical School reports obstructive sleep apnea, which is the most common type of sleep apnea, raises your heart rate and increases your blood pressure, putting stress on your heart.
One of the most notable symptoms of OSA is snoring. “It’s extremely rare for this condition to be fatal,”says Budhiraja. However, OSA is related to a host of other issues, such as high blood pressure, obesity, diabetes, heart attacks, stroke, increased traffic accidents, depression, anxiety, and, of course, insomnia. Treating sleep apnea, affirms Budhiraja, can alleviate the symptoms of depression and anxiety.
Treatments for OSA |
| The treatments for mild cases of sleep apnea focus more on making lifestyle changes that may be interrupting your sleep. These include losing weight (if you are obese or overweight), exercising on a regular basis, reducing alcohol consumption (if not stopping altogether), and quitting smoking. Other suggested treatments include changing your sleep position and using a nasal decongestant or allergy medication. The most common treatment for severe OSA is continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy, prescribed by your physician. The CPAP machine facilitates the constant flow of air into your throat so your airway remains open while you sleep. |
Restless Leg Syndrome
The third sleep disorder is Restless Leg Syndrome (RLS) that frequently disrupts sleep and affects 2-15% of the population. Sufferers describe an unpleasant and sometimes painful tingling or cramping sensation in the legs when resting or falling asleep at night. Moving the legs alleviates the symptoms but they quickly return when the movement stops.
The pain and discomfort often keeps people from sleeping at night. Researchers are still investigating what causes RLS, but there may be a link to iron deficiency, diabetes, high blood pressure, and ADHD, among other conditions. “Some types of antidepressants may also cause RLS,” says Budhiraja.
Treatments for RLS |
| Budhiraja recommends massaging your legs, taking a warm bath or shower, and doing light exercise and stretching to relieve the symptoms. More strenuous exercise, however, can worsen RLS symptoms and sleep quality, and should be avoided within 5-6 hours of bedtime. He also recommends making certain lifestyle changes including the elimination of caffeine, alcohol, and smoking cigarettes from your daily routine.
There are prescription medications available to treat RLS. One class of such medications are dopamine agonists that mimic the neurotransmitter, dopamine, in the brain. |